Top 10 technology trends for 2025

With technology advancing at breakneck speed, leaders are under immense pressure to balance innovation with practical execution. As 2025 approaches, CIOs and their teams are making complex decisions about which technologies to prioritize. To guide these critical decisions, we identified the top 10 emerging trends at the intersection of innovation, execution, and measurable business outcomes. Grounded in conversations with CIOs, the following insights reflect current priorities, challenges, and strategic directions of today’s technology leaders.
Top 10 technology trends for 2025
AI-accelerated everything: Accelerating innovation with AI-powered agentic development
AI is no longer a buzzword—it’s a proven catalyst that’s accelerating advancements across every sector. In the finance industry, AI is transforming how organizations identify market trends, optimize trading strategies, and enhance fraud detection. In retail, companies are using AI to create personalized shopping experiences, while in industries like finance, transportation, and natural resources, AI is enabling dynamic pricing strategies.
In software development, AI’s impact is transformative, particularly with the rapid adoption of coding assistants. At Slalom Build, for example, we’ve seen a 30%–50% increase in team velocity and a 20%–30% reduction in project costs by integrating AI into our engineering processes. But the real potential lies in advanced AI tools—like interactive, automated agents—that can accelerate the entire software development lifecycle (SDLC) five- to tenfold. These powerful tools go beyond assisting with code to generating use cases, automating test cases, modernizing legacy code, and optimizing deployment strategies. This is where AI truly transforms software engineering.
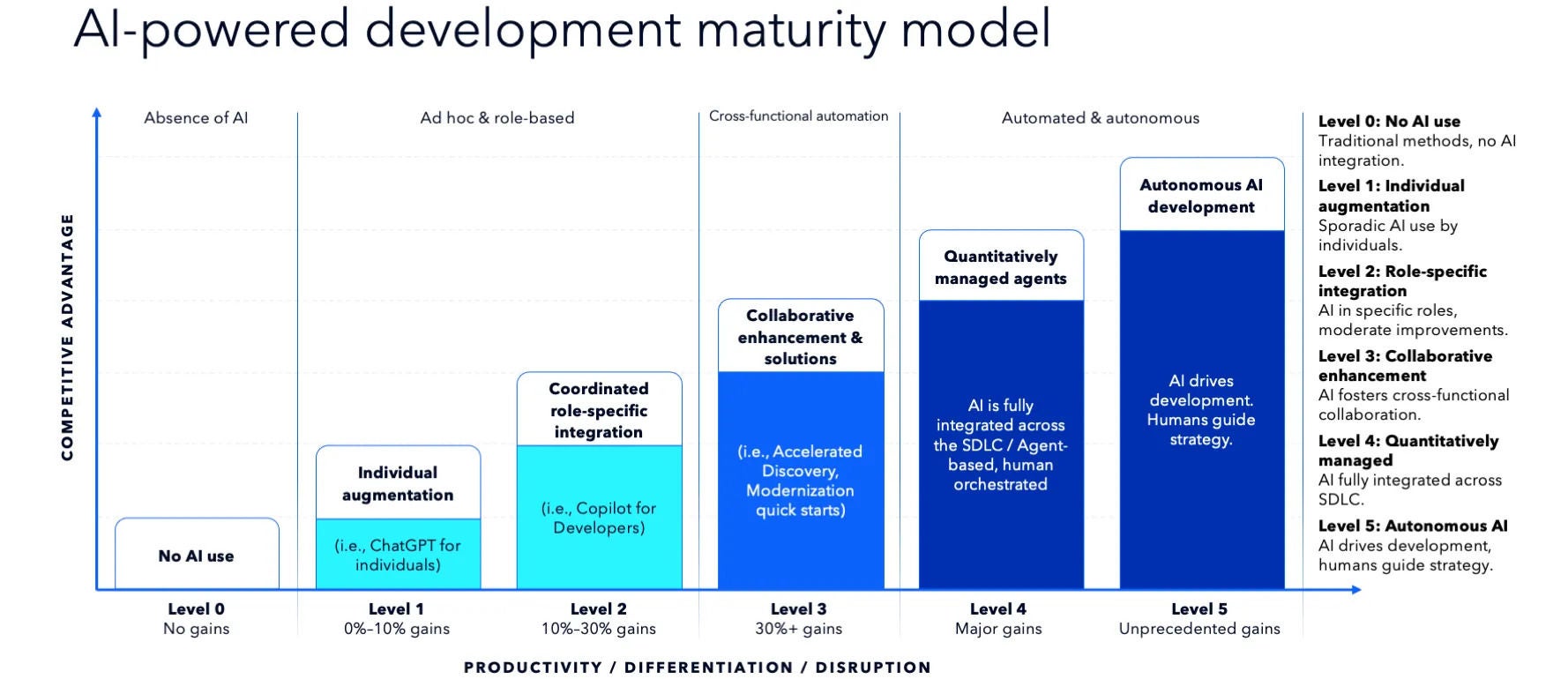
However, realizing this potential requires careful implementation to address challenges like preparing teams and processes, managing rapid development cycles, and avoiding the homogenization of products and customer experiences. With a strategic approach, AI can drive innovation, streamline workflows, and open new market opportunities while ensuring that differentiation remains intact.
Key considerations for CIOs:
- AI-readiness: Ensure your organization has the necessary infrastructure, training, and readiness to integrate AI-powered development tools effectively. Without this foundation, the rapid integration of AI could lead to inefficiencies or missed opportunities.
- Absorption of development speed: Establish strategies to manage the accelerated pace of AI-driven development. This includes robust monitoring and evaluation mechanisms to prevent disruption to existing teams and processes as development cycles shorten.
- Capacity utilization: Strategically plan how to utilize the extra capacity generated by AI, whether that means increasing output, reallocating capacity to other areas, or shifting focus toward growth.
- Customer experience differentiation: Deploy AI in ways that create unique, market-differentiating experiences. Identify where AI can enhance customer value, helping your offerings stand out while reinforcing brand loyalty.
Innovation overload: The risks of AI hype in technology investments
The pressure to adopt the latest technologies has always been present, but with the rise of GenAI, it’s now exponentially amplified. Companies are under pressure from all sides—employees, customers, boards, and executives—to invest in AI, often before the return on investment (ROI) or specific use cases are clear. In our 2024 survey of 200 C-suite executives, 82% indicated plans to increase AI investments in 2025, up from 70% in 2023. Yet this aggressive push risks resulting in rushed decisions and disconnected investments that may not deliver measurable value.
Despite the rapid adoption of AI-driven tools and copilots, many companies are finding their data, infrastructure, and quality assurance systems unprepared to support these technologies, leading to underperformance. Traditional quality control methods struggle to manage the vast content outputs of GenAI, often missing accuracy and reliability standards. High-profile failures have shown the risks of premature AI deployment, with consequences for brand reputation and, in some cases, safety.
For CIOs, the challenge is balancing the urgency for AI adoption with ensuring that investments are grounded in realistic business cases and backed by robust internal capabilities. The lesson is clear: AI should be adopted where it aligns with strategic goals, avoiding the pitfalls of adopting technology without fully considering readiness and integration.
Key considerations for CIOs:
- ROI and business case alignment: Ground AI investments in a clear ROI and business outcome alignment. Avoid decisions driven purely by external pressures to ensure that AI initiatives drive measurable value rather than being reactive.
- Data and system readiness: Is your data infrastructure and quality assurance framework ready to effectively support GenAI tools? Ensuring robust data and system support is critical to maximizing the effectiveness of GenAI tools and reducing the risk of poor performance.
- Change management: Develop and implement comprehensive change management strategies, including structured training and support. These steps are essential to ensure that AI tools are smoothly integrated into business processes and adopted effectively across teams.
- Brand and risk management: Anticipate and manage the risks associated with AI deployment. Protect your brand reputation by establishing controls and quality checks to mitigate potential underperformance and ensure AI tools enhance rather than detract from customer trust.
Hyperautomation: Automating the mundane and beyond
Hyperautomation takes traditional automation to the next level by integrating advanced technologies like AI, machine learning (ML), and robotic process automation (RPA) to automate entire business processes end-to-end. By leveraging AI-driven chatbots for customer inquiries, RPA for repetitive tasks such as data entry, and ML models for real-time anomaly detection, hyperautomation boosts efficiency, cuts operational costs, and frees human resources for higher-value work. Industries from healthcare to finance and more are seeing the impact; for instance, Celink, supported by Slalom, leveraged advanced automation to transform loan servicing, reducing costs and improving the customer experience. This innovation exemplifies hyperautomation’s potential to streamline complex processes and drive meaningful outcomes.
Hyperautomation’s success relies on robust data foundations. From structured CRM data to unstructured content like audio, video, and PDF documents trapped in your business applications, effective automation is only as strong as the quality and accessibility of a company’s data. Integration with data lakes, vector databases, and traditional databases allows the next frontier of AI to tap into this information seamlessly, enabling real-time responses to users’ needs.
However, hyperautomation is not without challenges. Businesses must balance automation’s power with adaptability, as overly rigid systems can falter when unexpected changes arise. To realize hyperautomation’s potential, organizations must plan carefully, ensuring flexible workflows that can respond to evolving needs without compromising efficiency.
Key considerations for CIOs:
- Data readiness: Ensure your data ecosystem, including unstructured data sources, is optimized for seamless integration with AI/ML automation.
- Established vs. evolving processes: Prioritize automation efforts on predictable, high-impact processes but ensure agility in evolving areas to avoid inefficiencies.
- Balancing automation and flexibility: Ensure automation systems are designed to adapt to evolving business processes. Maintaining flexibility and incorporating human intervention where needed will allow automation to complement rather than constrain dynamic workflows.
- Human in the loop: Identify where human oversight is essential, especially within complex workflows. Involving human expertise ensures that critical decision points are managed thoughtfully, particularly in nuanced or sensitive operations.
Connect the dots: Operating at the edge
The Internet of Things (IoT) and edge computing are transforming industries by enabling real-time intelligence at the edge of networks, where data is generated. This decentralized approach supports immediate decision-making, reduces latency, and minimizes bandwidth costs by processing data locally on edge devices like sensors, mobile phones, and AI-powered cameras. Any device capable of processing data locally, such as a mobile app on a smartphone, can function as an edge device. For instance, customer applications in app stores perform many functions directly on the device, while key data—like alerts and usage metrics—are sent back to the business. The number of devices managed at the edge is growing exponentially, creating new opportunities for efficiency and responsiveness across these sectors.
In industries such as retail, healthcare, and manufacturing, edge computing is already driving efficiency. For example, edge devices near point-of-sale (PoS) systems allow for quick transactions and real-time inventory updates in stores. Similarly, AI-enabled cameras positioned to detect wildfire smoke process data locally to deliver rapid alerts, critical for proactive disaster management.
While IoT creates connectivity, edge computing empowers localized intelligence, reducing dependency on centralized servers. However, scaling IoT and edge solutions across organizations presents challenges, particularly in integration, security, and interoperability. With 53% of organizations facing issues in integrating IoT with legacy systems, ensuring compatibility through open protocols is crucial. Additionally, securing each edge device is essential to protect the network from vulnerabilities.
Key considerations for CIOs:
- Integration and interoperability: Prioritize flexible, open standards and vendor-neutral solutions when connecting IoT and edge devices to legacy enterprise systems, preserving long-term adaptability.
- Security and privacy: Implement robust security protocols for all edge devices to safeguard data at its source. Ensure that your privacy strategy effectively manages edge data, minimizing unnecessary transmission and enhancing overall data security.
- Cost-benefit assessment: Evaluate the total cost of ownership of edge computing, factoring in device, connectivity, and maintenance costs to understand the true cost-benefit.
- Cloud-edge orchestration: Establish a robust hybrid infrastructure that optimizes data flows and workload distribution between cloud and edge locations, maximizing overall system performance and reliability.
Autonomous agents: Your digital partner
Autonomous agents mark a major evolution in AI, enabling systems to act, learn, and make decisions with minimal human oversight. These agents are transforming workflows across industries, from customer service to operational efficiency. However, the future of autonomous agents isn’t about removing humans entirely—quite the opposite, in fact. It’s about finding the right balance between automation and human involvement to ensure transparency, trust, and ethical use.
In customer service, for instance, autonomous agents like Virgin Voyages’ Vivi, a GenAI-powered digital human built on Salesforce with Slalom’s GenAI framework, can manage complex, real-time interactions while allowing for human intervention as needed. Decision-making frameworks, such as explainable decision trees, add transparency and help maintain trust—especially critical in sectors like healthcare, where outcomes must be clear and accountable.
While autonomous agents promise long-term benefits like cost savings and operational efficiency, they also introduce challenges, including job displacement, ethical concerns, and potential bias. Without robust governance frameworks and human oversight, these risks can outweigh the benefits. Successful implementations will leverage autonomous agents for routine tasks, while preserving human input in essential areas like decision-making, oversight, and customer interactions, achieving a balanced and responsible approach to automation.
Key considerations for CIOs:
- Governance and oversight: Establish governance frameworks to monitor autonomous agents, ensuring they operate with transparency, trust, and reliability. Define where human oversight is essential to maintain quality and uphold ethical standards.
- Explainability and bias prevention: Implement measures to make autonomous agent decision-making clear and explainable, with a focus on bias prevention — especially in regulated industries where transparency is critical.
- Strategic investment: Invest in autonomous agents strategically to stay competitive. Focus on deploying agents in areas that deliver measurable impact, balancing innovation with customer-centric design to ensure automation aligns with your brand’s values.
Build versus buy in the AI era
The build versus buy decision has become increasingly complex as AI reshapes the technology landscape. Traditionally, companies without engineering strength leaned toward buying vendor solutions rather than building custom software. However, GenAI is disrupting this balance, opening new opportunities for companies to develop their own AI-driven tools and solutions.
While AI-powered SaaS offerings continue to evolve, some organizations are opting to build custom solutions to address immediate workflow needs. AI has significantly reduced the cost of developing, debugging, and maintaining software, in some cases by as much as 50%. For companies with the right capabilities, building can create competitive advantages, especially when it leads to proprietary systems that differentiate the business. However, building only adds value when it aligns with clear business goals and delivers tangible ROI. Companies that lack the internal resources to maintain custom-built solutions may still find it beneficial to wait for SaaS providers to catch up—unless a custom build offers a critical advantage.
Still, the “buy” approach isn’t without challenges. The proliferation of departmental purchases, or “shadow IT,” can drive up costs and create fragmented ecosystems that are difficult to govern. CIOs must navigate this growing complexity, balancing the strategic benefits of building proprietary systems with the potential hidden costs and governance issues that can come from widespread, uncoordinated software acquisition across the organization. Ultimately, the decision between building and buying should be guided by available resources, strategic priorities, and a clear focus on business outcomes, not merely the accessibility of AI.
Key considerations for CIOs:
- Engineering capacity: Does your organization have the engineering talent and resources to build and maintain custom AI solutions? Without a strong technical foundation, building custom solutions could overextend your team and impact long-term sustainability.
- Cost-effectiveness of GenAI: Weigh the costs of building custom AI against waiting for SaaS providers to deliver mature AI solutions. If vendor offerings are delayed or priced too high, building may be the more cost-effective option; otherwise, waiting could save both time and resources.
- Strategic differentiation: Prioritize building only if it will offer a significant competitive advantage or unique value that aligns with business goals, rather than building solely for the sake of innovation.
Cloud cost crunch: Cutting cloud expenditures without compromising performance
As cloud adoption continues to rise, managing cloud expenditures is a growing concern for CIOs. Recent studies indicate that cloud spending frequently exceeds estimates by 30% due to factors like GenAI and other high-demand applications. This has prompted a reevaluation of cloud strategies as companies look for ways to optimize spending without sacrificing performance.
FinOps has become a highly effective strategy for managing cloud costs, bringing finance and cloud operations together to improve visibility into usage and spending. For instance, we partnered with a Fortune 500 insurer to unlock a 33% reduction in EBS volume costs, through targeted usage monitoring and spending optimization.
Additionally, multicloud strategies, though popular for reducing vendor lock-in, can complicate cost management. Companies are increasingly considering single-vendor solutions or edge computing options to minimize inefficiencies and reduce costs associated with data egress and duplicated workloads. These approaches, including edge processing, reduce reliance on cloud data transfers and can significantly lower expenses by handling data closer to its source.
These trends highlight the importance for CIOs of not only managing cloud growth but also aligning spending with strategic needs through improved cost governance and streamlined architecture choices.
Key considerations for CIOs:
- FinOps integration: Does your organization have a FinOps strategy in place to ensure visibility, cost control, and accountability in cloud spending? A structured approach to financial operations helps maintain budget alignment and prevents unexpected costs.
- Modernizing cloud infrastructure: Evaluate whether your cloud infrastructure needs modernization, such as adopting serverless computing or platform services to reduce costs.
- Multicloud vs. single vendor: Assess the efficiency of your multicloud strategy. If duplicated workloads or frequent context switching are causing inefficiencies, consolidating with a single vendor may reduce complexity and optimize costs.
- Data egress optimization: Implement strategies to manage data transfers effectively and minimize egress costs, particularly for data moving between on-premises systems and the cloud. Optimized data flows reduce unnecessary expenses and improve overall cost efficiency.
Zero trust and mesh architecture: Enhancing detection and response to cyber threats
As cyber threats grow in frequency and sophistication, AI is reshaping the cybersecurity landscape—not only by enhancing threat detection and response capabilities, reducing human-based errors, and improving incident response velocity but also as a tool for adversarial vectors to identify and exploit vulnerabilities. This dual role of AI, as both a threat and a defense mechanism, underscores its critical role in modern cybersecurity. Integrating AI into zero trust and mesh architectures enables continuous monitoring and real-time response, proactively defending against attacks while maintaining system integrity.
In today’s environment, where remote and hybrid work has expanded the attack surface, AI-enabled security strategies have become essential. Attackers increasingly use AI to identify vulnerabilities, making it critical for organizations to adopt equally advanced technologies for defense. AI strengthens real-time detection capabilities, reduces time to detect (MTTD) and time to response/recover, and minimizes the false error rate, helping to streamline security operations and ease the burden on human teams.
Combining AI with zero trust’s continuous verification and mesh architecture’s network segmentation allows organizations to limit the impact of breaches, prevent lateral movement within networks, and better protect sensitive data. These AI-driven strategies create a resilient security posture, adapting to evolving threats to ensure critical systems remain secure.
Key considerations for CIOs:
- AI-enhanced defense: Integrate AI/ML into cybersecurity strategies to proactively detect anomalies and counter emerging AI-driven threats. AI-powered defense provides the agility needed to respond to increasingly sophisticated attacks.
- Integration with other security tools: Transitioning to zero trust and mesh architectures can be complex, especially for hybrid environments. Effective zero trust requires seamless integration with other security tools to ensure a robust defense. CIOs and CISOs should ensure AI systems work well with firewalls, intrusion detection, SIEM, identity access management, data protection, and other security platforms.
- Customer trust and compliance: Develop a zero trust strategy that not only enhances data security but also aligns with regulatory requirements and fosters customer trust, supporting compliance and protecting your brand reputation.
One platform, infinite possibilities: Unified data processing and visualization
As businesses navigate increasingly complex data landscapes, unified data platforms from all the hyperscalers and specialized data platforms like Snowflake and Databricks are transforming how data is managed and leveraged for decision-making. Traditional methods of moving, copying, and duplicating data across systems are giving way to more efficient architectures. Zero-copy strategies, for instance, allow data to be queried directly at the source, reducing costs and providing decision makers with real-time, trusted data—an essential factor for AI/ML initiatives.
CIOs now face the task of aligning their data strategies to support this unified approach. Beyond cost savings, a unified platform enables seamless integration of AI-powered insights across business units, driving faster and more informed decision-making. However, adopting these architectures requires systems capable of balancing multicloud flexibility with the simplicity of single-cloud deployments.
Effective governance and security are central to this transition. By implementing a centralized data governance framework and enabling data access at its source, organizations can innovate faster, reduce operational overhead, and lower security risks. This alignment of governance with platform readiness positions businesses to be more agile and competitive in a rapidly evolving landscape.
Key considerations for CIOs:
- Enabling real-time insights: Does your system architecture support zero-copy strategies to access data in real time? Timely data accessibility is essential for responsive and informed business operations.
- Unified governance and ownership: Establish robust governance frameworks to manage decentralized environments effectively. Maintaining accountability across diverse data sources ensures data integrity and supports compliance in complex, multicloud or hybrid environments.
- Optimizing data security: Centralize security efforts to reduce redundancy, enhance compliance, and maintain consistent security standards across platforms and environments. A unified security approach strengthens data protection and minimizes risks across the organization.
Workforce reimagined: Transforming employee empowerment and workplace efficiency
Automation and AI are reshaping the workforce, enabling employees to move beyond routine tasks and focus on high-value, strategic work. AI-driven tools boost productivity, enhance job satisfaction, and create a more adaptable workforce that’s better equipped to meet the demands of an evolving digital landscape.
As AI becomes more embedded within organizations, the demand for certain skills is shifting. While technical expertise like software development was prioritized in 2023, our 2024 research highlights a growing emphasis on critical thinking, problem-solving, collaboration, and teamwork. This shift reflects a broader recognition that creativity, adaptability, and effective collaboration are essential for fully harnessing AI’s potential. Leaders play a crucial role in fostering this shift by promoting a culture of continuous learning and adaptability.
Reimagining the workforce delivers value beyond efficiency gains; it drives strategic focus, boosts job satisfaction, and fosters innovation. By automating routine tasks, businesses can unlock employee potential, enabling teams to concentrate on innovation and strategic decision-making. Active leadership involvement is essential to ensure a successful transition to an AI-empowered workforce.
Key considerations for CIOs:
- Workforce adaptability and culture of innovation: Prioritize developing a strategy that aligns AI-driven tools with existing workforce capabilities. Partner with HR to implement training programs that upskill employees, ensuring they are prepared to transition into more strategic roles that AI enables.
- Resource allocation: Develop a multiyear road map that prioritizes immediate AI training needs alongside long-term infrastructure investments. Strategic resource allocation ensures sustainable progress and supports future AI scalability.
- Balancing automation and human expertise: Define clear boundaries between tasks suited for automation and those requiring human expertise. Maintaining this balance preserves quality and leverages human skills where they add the most value.
Key takeaway
As these trends highlight, today’s CIOs face unprecedented choices that will shape their organizations for years to come. This isn’t merely about adopting new tools but about cultivating a balanced approach to innovation — one that supports strategic objectives, operational resilience, and employee empowerment. By prioritizing technologies that offer both measurable ROI and the flexibility to evolve, CIOs can navigate the complexities of a changing landscape with confidence.
Expert contributors: Dave Cutler, Sarah Duffy, Anthony Gould, Pez Nikpour, Allen Mann, and TC Sutton
Slalom is a fiercely human business and technology consulting company that teams with leaders who expect more. So we bring more.



